
发布时间:2022-04-26
A. 简介
瑞士高度重视公立教育。由于受到政府资助,瑞士公立教育常常被认为比任何著名的私立寄宿学校都要优质。瑞士高度重视免费公立教育的重要性,这也是瑞士在教育领域享有盛誉的重要原因。考虑到瑞士公立教育系统的复杂性,以及孩子们在择校时所面临的众多可能,雷梭勒家族办公室希望通过本文件介绍瑞士公立教育系统,帮助家族做出正确的选择,使家族下一代能够更好地融入瑞士社会。

1. 学校的使命
学校负责所有学生的教育、指导以及文化知识的传播,确保学生积累知识、获得技能,使每个人都能充分发挥自己的潜能。
为此,学校特别在以下方面开设了相关课程,确保学生的发展:
法语/德语文化,涉及阅读和写作的能力,口头与书面理解和表达的能力;
语言技能与文化,包括用外语进行口头与书面交流的技能;
数学文化,包括对基本数学概念和方法的掌握,设计情境和解决问题的能力;
基于人文社会科学和自然科学的科学文化;
艺术文化,涉及对各种形式的文化遗产的感知和表达,包括视觉、造型艺术和音乐;
体育知识,确保并保持身体健康。
学校的目标主要在于帮助孩子获得知识和技能、技术和方法,培养他们的体能,同时通过让孩子对自己和周围世界建立认知,塑造他们的判断力和个性,促使他们在社会中找到自己的定位。
2. 愿景与价值观
学校提倡创造一个有利于学习的和平的校园环境,旨在在对话与尊重的基础上,唤起学生们的好奇心、责任感和自主性,促使每位学生都能实现个人的发展。
核心价值观:

B. 结构

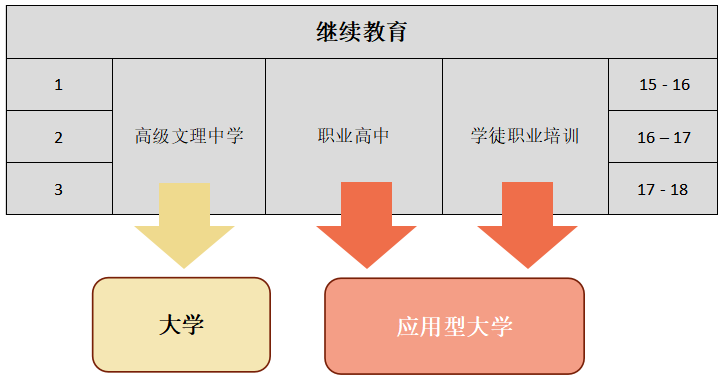
瑞士的教育体系非常灵活。
无论你选择哪种方案,都有可能进入大学学习。
C. 义务教育系统(4-15岁)
1. 小学
1至8年级为小学阶段(普通教育)。小学教育的第一阶段致力于学生的初步发展,在娱乐与教学相结合的环境中培养他们的技能。孩子们将会逐步学习基本的社交技能和学习方法。他们完成第一年学业所需的时间取决于他们的智力发展与情感成熟度;如果有必要,孩子们将会得到特殊措施的支持。
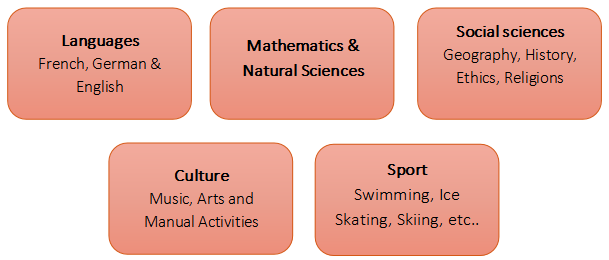
在小学教育的下一个阶段,孩子们会逐渐接触不同的科目。幼儿园或小学阶段后教授的科目一般有以下几项:
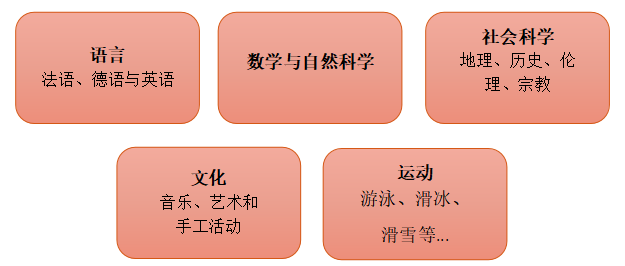
原则上,一个班级只安排一名教师密切关注学生的进步情况。在义务教育的前6年里,孩子们的表现由教师通过个人评估进行衡量。
外国孩子特别班:
因语言或学术知识不足,难以直接融入普通班级的5-11岁的外国学生有机会参加预备班。这些班级将会尽可能早地提供法语、数学学习,巩固并提升必要的学校知识,使学生能够成功融入到与他们的年龄和能力相适应的普通班级中。
1.1 中学预科教育(7-8年级)
这一阶段是为进入中学做准备。为此,将会设立一个教育团队负责一个班级的学生,陪伴他们度过两年的学习时光(原则上是在同一个学校)。这一教育结构与使用法语教学的课程相一致,确保通过这两年的学习更好地保持教学上的连贯性。
1.2 中学
根据学生小学毕业时的表现、老师的推荐(可能还会有过渡性考试),班级的水平会有所不同:根据成绩水平不同进行分班定制化教育。
中学阶段旨在培养年轻人的个性,鼓励他们不断学习,增强他们的责任感,培养他们的主动性,教授他们发现并解决问题、处理冲突、独立工作以及参与小组工作的能力。此外,这一阶段也是为学生过渡到继续教育做准备。
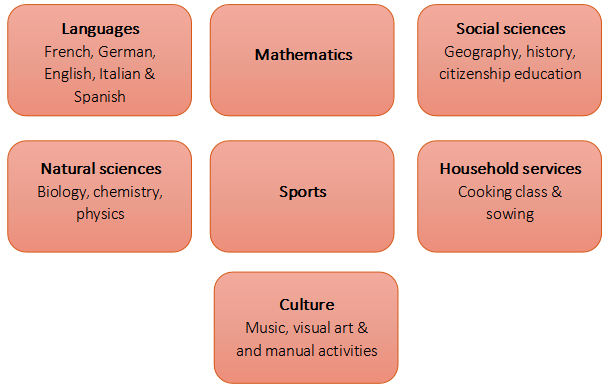
中学阶段的教学内容包括以下学科领域和分支:
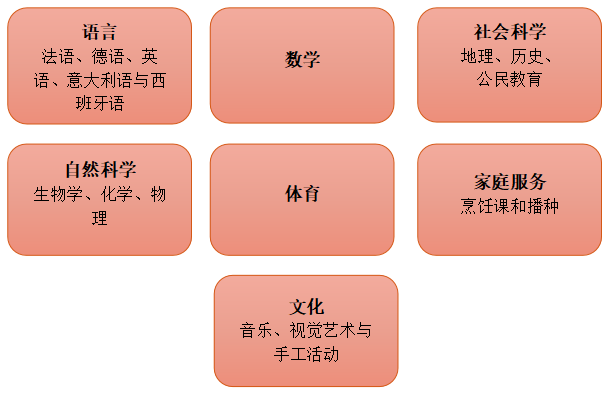
2. 教育支持
各州负责为有特殊教育需求的孩子和青少年提供学校教育。每个州都有自己的标准专业教育措施,以满足孩子的特殊需求。
3. 新技术
手机和电子设备的使用须遵守以下规定:
计算机网络受到保护和监控;
每个学生都有权使用学校发放的学生系统密码;
家长须对孩子手机和其他设备的滥用负责。
4. 图书馆
每个学校中心都有一个适合学生的图书馆。若学生希望将图书馆的书借阅回家观看,图书管理员会提供帮助。
5. 学校生活
学校能为学生组织各种活动,以提高他们对文化、社会和自然环境的认识:

6. 行政管理
6.1 意外险
家长有责任通过自己的健康保险或私人意外险来承担全部的意外风险。因此,学校不承担学生的意外险。发生任何事故都将由家长直接向学生所投保的健康与意外险公司报案。
6.2 个人责任险
对建筑物、家具和设备造成的任何损坏,将由责任人承担维修费用。造成损坏的学生的家长或法定监护人要对此负责,因此强烈建议学生家庭购买第三方保险。
6.3 眼镜破损
在学校里(体育课、运动课或娱乐活动中)发生眼镜破损的情况,学校不予赔偿。
6.4 公共交通
使用公共交通工具的费用由家长承担。有些城市会对购买旅行卡给予补贴。
Original English Text
Swiss Public Schools System
A. Introduction
The Public Education is highly valued in Switzerland and is considered better than any of the prestigious private boarding schools thanks to government funding. Switzerland highly values the importance of free, public education available to anyone which is what gives Switzerland its high reputation. This document is to informed about the Swiss public education system. Due to its complexity and the many possibilities the children are exposed to, La Soleille Family office role is to assist the families in making the right choice for the integration of next generation in the Swiss Society.
1. The School's Mission
The school is responsible for the education, instruction and cultural transmission of knowledge for all pupils. It ensures the building of knowledge and the acquisition of skills enabling each individual to develop his or her potential to its fullest.
In particular, the school establishes and ensures the development of:
a French culture involving the ability to read and write, as well as the capacity to understand and express oneself orally and in writing;
Language skills and culture including oral and written communication skills in a foreign language;
a Mathematical culture involving the control of basic mathematical concepts and approaches as well as the ability to design situations and solve problems;
a Scientific culture based on both the human and social sciences and the natural sciences;
an Artistic culture combining perception and expression of the various forms of the cultural heritage, both in the visual and plastic arts and in music;
Sport knowledge that ensure the well-being of the body and the preservation of its health.
The school aims in particular to enable the child to acquire knowledge and skills, techniques and methods to develop his or her physical abilities. It shapes their judgement and personality, through awareness of themselves and the world around them, to enable them to find their place in society.
2. Vision & Values
The school circle promotes the creation of a peaceful school environment that is conducive to learning. The aim is to awaken curiosity, a sense of responsibility and autonomy to allow for the personal development of each individual, based on dialogue and respect.
The core values are:

B. Schema
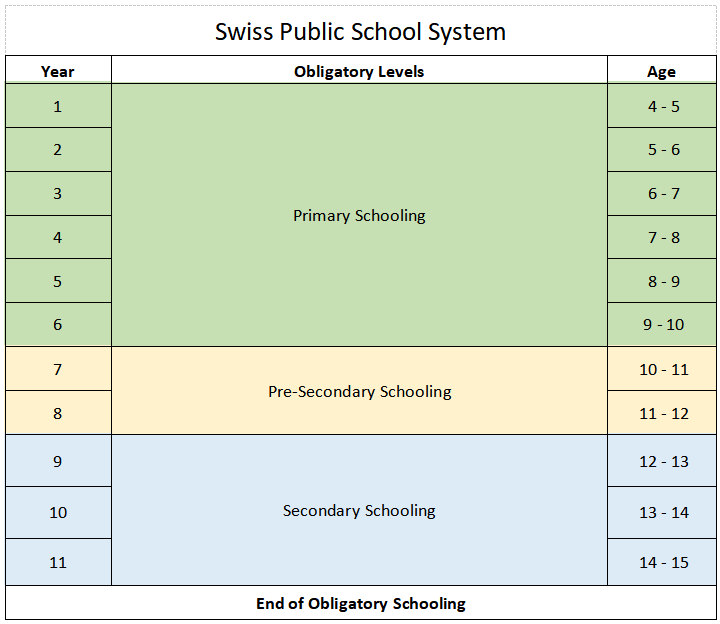
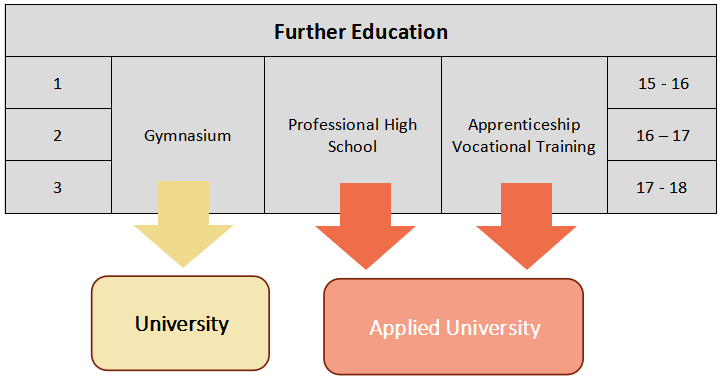
Swiss Education System is very flexible.
No matter which option you select, studying at the University is still possible.
C. Mandatory School System (4-15 years old)
1. Primary School
Years 1 to 8 are the primary level (regular education). The first phase of the education of the pupils is dedicated to their initial development. Skills are fostered through a recreational and pedagogically stimulating environment. The children learn the basic social skills and school work methods step by step. The time they need to complete the first years of school depends on their intellectual development and emotional maturity; if necessary, children are supported by special measures.
During the next phase of primary level, the children are gradually introduced to different subjects. The subjects taught after the kindergarten or elementary cycle are generally the following:
In principle, only one teacher is assigned to a class to closely follow the progression for the pupils. During the first 6 years of their schooling, the children’s performance are measured based on the teachers personal assessment.
Special classes for foreign language children:
From age 5 to 11, foreign language pupils whose linguistic and sometimes academic knowledge is insufficient to enable them to be integrated directly into the regular classes have the opportunity to attend reception classes. These classes provide the earliest possible learning of French, mathematics, consolidation and upgrading of the school knowledge necessary. This enables a successful integration into a regular class corresponding to the age and possibilities of the pupil.
1.1 Pre-Secondary School - Year 7 to 8
This period is used to prepare for entry into secondary school. For this purpose, an educational team is responsible for the pupils in a class and accompanies them for two years, in principle in the same school. This structure, in line with the French-speaking curriculum, ensures a two-year learning process and greater pedagogical consistency.
1.2 Secondary School
Based on the performance at the end of primary school, the teacher's recommendation, and sometimes a transitional examination, the level of the classes will vary: Education is provided on the basis of performance levels.
Secondary level aims at developing the personality of young people and encourages them to learn more and more throughout their lives. It aims to strengthen their sense of responsibility, develop their sense of initiative and teach them to identify and solve problems, deal with conflicts and work alone or in groups. Additionally, it prepares students for the transition to further education.
The following subject areas and branches are taught at secondary level:
2. Educational Support
The cantons are responsible for the schooling of children and young people with special educational needs. Every canton has it’s own standard specialised education measures in case of special needs for the children.
3. New Technologies
The use of mobile phones and electronic devices is subject to regulation:
Computer networks are protected and monitored.
Each student is responsible for the use of his/her school issued password.
Parents are responsible for the misuse of mobile phones and other devices.
4. Library
Each school centre has a library suitable for students. Book lending at home is organized by the librarians.
5. School Life
Various activities can be offered to pupils to raise their awareness of their cultural, social and physical environment:

6. Administration
6.1 Accident Insurance
Parents are responsible for the full coverage of accident risks through their own health insurance or private accident insurance. Consequently, students are not insured against accidents at school. Any accident will be reported directly to the student's health and accident insurance by the parents.
6.2 Personal Liability Insurance
Any damage caused to the buildings, furniture and equipment will be repaired at the expense of the person responsible. A pupil who causes damage is liable to his/her parents or legal guardian. It is strongly recommended that the family take out third party insurance.
6.3 Eyeglasses breakage
Breakage of eyeglasses at school (physical education and sports lessons, recreation, etc.) is not compensated by the school.
6.4 Public Transport
The use of public transport is at the parents' expense. Some municipalities subsidise the purchase of a travelcard.
本文转载自雷梭勒家族办公室,如有侵权,敬请告知删除。
Sooswiss为您提供
瑞士方向私人管家式的定制服务:
1)家族传承 2)财富管理 3)瑞士投资
4)居留计划 5)税务优化 6)家族治理
更多资讯请登录网站 www.sooswiss.com
