
发布时间:2022-05-05
导语:
在上期的公众号中,我们为大家介绍了瑞士公立教育系统中的中小学义务教育。在本期的公众号,我们将接着介绍义务教育结束之后的高中教育以及高等教育。
D. 高中教育
1. 高级文理中学
1.1 简介
高级文理中学旨在培养学生在任何院系中进行大学学习的能力。学校的目标是为学生提供获得完备的基础知识的机会,培养他们的开放意识和独立判断的能力。高级文理中学提供均衡、连贯的通识教育,授予学生接受高等教育所需的高中文凭,让他们为承担社会责任做好准备。与此同时,这些学校还注重培养学生的智力、意志力、道德和审美感受力以及体能。
1.2 课程设置
高级文理中学课程整体包括:核心科目、特定选修课、补充选修课以及毕业论文。
在学习初期,学生可以在以下学科中选择不同的研究领域:
第二语言、第三语言。
“社会与经济科学”或“数学与实验科学”研究领域。
还可学习“艺术”和体育。
以下是相关学习科目:

语言(2科)+“社会与经济科学”或“数学与实验科学”(6或5科)+“艺术”(2科)+体育(2科)=11或12科 毕业
1.3 文凭认可
高级文理中学文凭的持有者具备进行大学学习所需的一般性知识与技能。特别是,这些文凭赋予了其持有者进入以下任何大学权利:
世界各综合大学
联邦理工学院
2. 职业高中
2.1 简介
瑞士的职业高中提供广泛的通识教育以及与各种高等教育专业领域相关的教育,以便学生能够为以后的继续教育提前做好准备。此外,职业高中还强调学生个性的发展。因此,课程设置侧重于能力的培养与获得、多样化的教学方法、适当的教育结构和专业实践。
职业高中将为以下专业领域的教育打下基础:
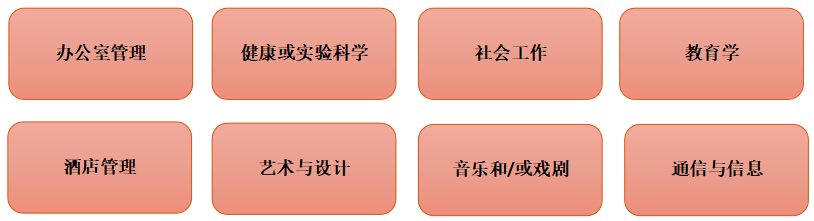
与专业领域相关的科目能够让学生为今后的学习和活动,以及在高等教育部门参加进一步培训做好准备。
2.2 使命
这些职业高中的使命是:
为学生提供全面的通识教育。
培养学生的个人技能及社交技能。
这些职业高中能够为学生提供专业领域所需的知识和技能,帮助他们为今后做好准备。
2.3 课程设置

课程设置选择与高级文理中学基本一致。
3. 学徒制
3.1 简介
学徒制是瑞士的双轨制体系,包括职业教育和培训两个部分,在允许年轻人在职业学校就读的同时,也允许他们在公司接受培训。它既能为年轻人提供高质量的培训,又能让他们直接进入劳动力市场,这也是瑞士经济如此成功的一个重要因素。由于职业的不同,学徒期有2到4年不等。可以说,完成这一课程的年轻人的失业率会大大降低。

3.2 进一步深造的机会
选择走学徒途径的人总是可以通过额外的课程提高他们的培训水平。职业道路多种多样,人人都可以选择。有了专业的高中毕业文凭,就有可能获得学士学位。因此,这些学徒也可以达到与大学或理工学院学生相同的水平。
但完成学徒期的人不一定需要继续学习。他们可以专注于他们所学的专业,并在专业学校进一步深造。因此,这些工人具有更高的资格、更好的职业前景,能够获得更高的工资。
在瑞士,学生们仍然可以凭借自身的专业经验得到职业晋升,而不仅仅是凭借自身的受教育程度。
E. 高等教育
1. 大学与联邦理工学院
瑞士有12所公认的大学:10所州立大学和2所联邦理工学院(ETH/EPFL)。大学是传统的学术性大学,主要从事基础研究,而应用科学大学则主要面向应用型研究。
学习所需语言:
→ 巴塞尔大学、伯尔尼大学、卢塞恩大学、圣加仑大学和苏黎世大学以及瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院(ETHZ)位于瑞士的德语区。
→ 日内瓦大学、洛桑大学和纳沙泰尔大学以及瑞士洛桑联邦理工学院(EPFL)位于瑞士的法语区。
→ 弗里堡大学位于弗里堡双语区(法语和德语)。
→ 提契诺大学(USI)位于讲意大利语的提契诺州。
如今,各专业硕士学位课程都是以英语授课,而在学士学位一般由瑞士本国语言(法/德/意)授课。

1.1 学士与硕士课程
根据《博洛尼亚宣言》,瑞士大学教育遵循双阶段模式(two-cycle model),即提供本硕连读课程。该宣言允许欧洲大学的学生自由进入其他欧洲大学学习。学士全日制学习的时间一般为三年,硕士全日制学习则需要一年半到两年的时间。
1.2 本科录取条件
各州大学和联邦理工学院在录取本科生时,要求有瑞士高中文凭或同等学历证书,并且应当熟练掌握学习所需的语言。每所大学都规定了具体的录取要求。
在瑞士,所有课程的录取都是不受限制的,只有少数课程(医学研究、脊椎按摩、某些体育及运动科学)例外。对于有入学考试的课程,每年都会根据申请人数决定是否需要考试。由于学习名额有限,对外国学生(非瑞士居民)有特殊的录取要求。
1.3 硕士录取条件
攻读硕士学位需要先取得学士学位。硕士阶段的学习可以在本科就读学校进行,也可以在另一所大学进行。原则上,硕士阶段的学习可以更改本科研究方向,因此,在录取之前,学生可能需要在本科期间掌握额外的知识和技能。要想从不同专业类型的大学转学,必须符合明确规定的条件及额外要求。
1.4 博士录取条件
对于某些硕博连读专业,学生完成硕士学位课程并达到一定额外要求后,可直接进入博士研究阶段。各个大学负责自己的博士生录取工作。如果科研资格足够,拥有其他类型大学的硕士学位也可以进入博士阶段学习。
2. 应用科技大学
除了传统的大学之外,瑞士还有另一类大学——应用科学大学。这类大学提供以实践和应用为导向的学习课程,为学生提供专业资格。应用科学大学在各个领域提供以实践为导向的学士与硕士课程,以及广泛的继续教育的机会。在瑞士有8所区域性的应用科学大学,它们为那些已经完成初步职业培训并已取得职业高中文凭的人提供了进入大学学习的机会。
2.1 学士与硕士课程
根据《博洛尼亚宣言》,应用科学大学教育也按照双阶段模式,提供本硕连读课程。与传统大学不同的是,应用科学大学不提供博士课程。
学士课程通常可以获得授予专业资格的文凭。学习期间,学生们可直接参加专业实践。全日制学习时间为三年,第四年为实习就业时间。
学士学位课程结束后,应用科学大学业提供硕士课程学习。硕士课程教授深入、专业、以研究为基础的知识,为学生获得高级专业资格文凭做准备,学习时间长达一年半。硕士课程的范围有限,因为帮助学生获得职业资格的学士学位仍然是应用科学大学的标准。

2.2 本科录取条件
录取条件详见《联邦大学促进与协调法》(the Federal Law on the Promotion and Coordination of Universities)和《应用科学大学录取条例》(the Ordinance on Admission to Universities of Applied Sciences)。
应用科学大学的录取不需要入学考试,但需要有与所选研究领域相关的职业高中文凭。没有完成相关职业初始文凭的学生,必须在该研究领域有至少一年的工作经验。
拥有高级文理中学文凭的毕业生,必须在与所学专业相关的职业中拥有至少一年的工作经验才能被录取。
2.3 硕士录取条件
硕士课程的录取要求在同一研究领域取得学士学位或同等学历证书。此外,应用科学大学还可能会设定额外的要求。
F. 私立教育学生、外国学生录取条件
对于私立教育学生、外国学生的录取和认可都有特定的要求。必须明确指出的是,在任何情况下,大学的录取要求都优先于瑞士国家评估。
国家评估提供的信息包括:具备哪些国家的高中毕业证书以及在哪些条件下,学生才有资格被不同的瑞士大学录取。这些评估只针对一年级的学生。更多录取信息由相关大学提供。

G. 结语
由于瑞士教育体系提供了各种可能,因此可以总结出瑞士教育的两大特点:
高度的灵活性:对于那些想要接受培训、更换学校或课程、完成另一学位的人来说,有多种途径可以选择;
开放的各种教育机会:如果学生具备必需的资格,他们就可以参加自己选择的课程;如果是高等教育,学生们也可以选择自己的研究领域。在职业培训方面,存在的少数限制是由于所提供的学徒名额有限;但在某些研究领域,限制性条件则是某些大学所实行的法定条款。
尽管瑞士公立教育系统看起来非常复杂,但却结构清晰、运作良好。选择瑞士公共教育,您能让您的孩子获得更加广泛的受教育的机会。

如果您有任何问题,可以咨询我们的教育顾问,他们有着第一手的瑞士教育系统经验,可以为您解答所有疑问。借鉴这些经验,我们将能引导您的孩子在学习和未来职业方面走上一条最佳的道路。
Original English Text
Swiss Public Schools System II
1. Gymnasium
1. Introduction
The goal of the gymnasium is to develop within the students the ability to undertake university studies in any faculty. The aim of the schools is to offer their students the opportunity to acquire a sound basic knowledge and to develop their open-mindedness and capacity for independent judgement. These schools provide a balanced and coherent general education, which gives students the maturity required to undertake higher education and prepares them to assume responsibilities in today's society. The schools simultaneously develop their students' intelligence, will power, ethical and aesthetic sensibility as well as their physical abilities.
1.2 Curriculum
The core subjects, the specific options, the complementary options as well as the maturity thesis make up the whole of the disciplines of the Gymnasium maturity.
At the beginning of their studies, students can choose different fields of studies:
A secondary and third language.
Field of study “social and economic sciences” or “mathematics and experimental sciences”.
They also are subject to the field of study “Arts” and physical education.
These are the following subjects:

1.3 Certificate recognition
Recognised certificates show that their holders have the necessary general knowledge and skills to undertake university studies. In particular, they give the right of admission to any:
- University
- Federal Institutes of Technology
2. Professional high school
2.1 Introduction
The professional high schools in Switzerland provide a broad general education and an education related to the various tertiary level professional fields for which it prepares students. In addition, the professional high schools emphasise personality development. The curriculum focuses on the development and acquisition of competences, on diversified teaching methods, on appropriate school structures and on professional practice.
The professional high schools prepare for education in the following professional fields:
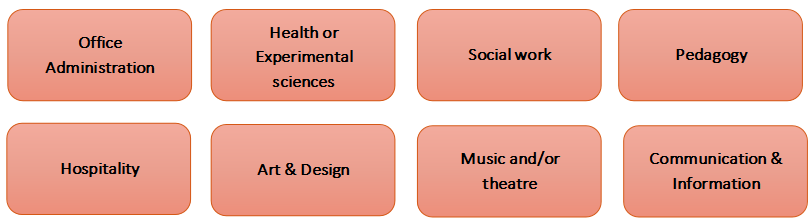
The subjects related to professional fields prepare students for their future area of study and activity as well as for further training in the tertiary sector.
2.2 Mission
The mission of these professional high schools is:
To equip students with a thorough general education.
For students develop their personal and social skills.
To provide students with the knowledge and skills specific to the professional fields for which these professional high schools prepare them for.
2.3 Curriculum

3. Apprenticeship
3.1 Introduction
The apprenticeship, the Swiss dual system of vocational education and training allows young people to be trained in a company while attending a vocational school. It offers both quality training and direct access to the labour market, a success factor for the Swiss economy. Depending on the profession, an apprenticeship can last between two to four years. It guarantees a very low unemployment rate among young people who have completed this course.
3.2 Futher opportunities
Those who choose the apprenticeship route can always improve their level of training with additional courses. The career paths are varied and accessible to all. With the professional maturity diploma, it is possible to obtain a Bachelor's degree. These apprentices can therefore reach the same level as university or college students.
However, those who complete an apprenticeship do not necessarily need to continue studying. They can concentrate on the profession they have learned and further their education in specialized schools. These workers are therefore more qualified, have better career prospects and higher wages.
In Switzerland, you can still climb up the ladder thanks to your professional experience, not only thanks to your degree of education.
E. Higher Education
Universities and universities of applied sciences are responsible for education and training, research and development, as well as for providing services to third parties. There are two types of universities in Switzerland:
1. Universities & Federal Institutes of Technology
There are twelve recognised universities in Switzerland: ten cantonal universities and two Federal Institutes of Technology (ETH). Universities are traditional academic universities that are mainly concerned with fundamental research, in contrast to universities of applied sciences, which are mainly oriented towards applied research.
Language of Studies:
→ The universities of Basel, Bern, Lucerne, St. Gallen and Zurich as well as the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETHZ) are located in the German-speaking part of Switzerland.
→ The universities of Geneva, Lausanne and Neuchâtel as well as the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL) are located in the French-speaking part of Switzerland.
→ The University of Fribourg is located in the bilingual canton of Fribourg (French and German).
→ The Università della Svizzera italiana (USI) in the Italian-speaking canton of Ticino.
Today, variety of master degrees are available in English in different fields. However bachelor degrees are difficult to find in a non-national language.
1.1 Bachelors and Masters Programs
The education is carried out according to the two-cycle model, with bachelor and master programmes, in accordance with the Bologna Declaration which grants students from European universities free access to other European universities. The duration of full-time studies is generally three years. A further one and a half to two years of full-time study are required for Master's studies.
1.2 Bachelors Admission Conditions
To be admitted to bachelor's studies, the cantonal universities and the Federal Institutes of Technology (ETH) require a Swiss maturity diploma or an equivalent certificate as well as proficiency in the language of study. Each university defines the specific admission requirements.
In Switzerland, admission to all programmes is unrestricted, with a few exceptions (medical studies, chiropractic, certain sports and motor sciences). For courses with an entrance examination, a decision is made each year on the basis of the number of applications as to whether an examination is required. Due to the limited supply of study places, there are special admission requirements for foreign students (non-swiss resident).
1.3 Masters Admission Conditions
Admission to the Master's programme requires a Bachelor's degree. Master's studies can then be started at the same university or at another one. In principle, it is also possible to change direction. Before admitting a candidate, the university may require the acquisition of additional knowledge and skills. The transfer from another type of university to a university is linked to well-defined conditions and additional requirements.
1.4 PhD Admission Conditions
A Master's degree with additional requirements guarantees access to doctoral studies. Admission is the responsibility of the university. Access is also possible with a Master's degree from another type of university, if the scientific qualifications are sufficient.
2. University of Applied Sciences
In addition to traditional universities, Switzerland has a second type of universities. These are the universities of applied sciences, which offer practice-oriented and application-oriented courses of study and provide professional qualifications. They offer practice-oriented bachelor's and master's programmes in various fields as well as a wide range of continuing education opportunities. There are eight regional universities of applied sciences. The universities of applied sciences enable people who have completed their initial vocational training and obtained a vocational maturity diploma to study at a university.
2.1 Bachelors and Masters Programs
Education is provided according to the two-cycle model, with bachelor's and master's programmes, in accordance with the Bologna Declaration. Unlike traditional universities, universities of applied sciences do not offer PhD programmes.
Bachelor's programmes generally lead to a diploma that grants a professional qualification. They give direct access to a professional practice. Studies last three years full-time and four years in employment.
Universities of applied sciences offer master's programmes which follow the bachelor's programme. Master's programmes also impart in-depth, specialised and research-based knowledge and prepare students for a diploma that certifies their higher professional qualification. Studies last up to one and a half years. The range of master's programmes is limited as the bachelor's degree, which qualifies students for a profession, is still the standard at universities of applied sciences.
2.2 Bachelors Admission Conditions
The admission requirements are regulated by the Federal Law on the Promotion and Coordination of Universities and by the Ordinance on Admission to Universities of Applied Sciences.
Admission to a university of applied sciences without an entrance exam, requires a professional maturity diploma linked to the chosen field of study. Students who have not completed their initial diploma in this related occupation must have at least one year's work experience in the study’s field.
Graduates with a gymnasium maturity diploma are admitted only with at least one year's work experience in an occupation related to their studies.
2.3 Masters Admission Conditions
Admission to the Master's programme requires a Bachelor's degree in the same field of study or an equivalent degree from a university. Universities of applied sciences may set additional requirements.
F. Admission from Private Education/Foreign Countries
Admission and recognition from private education and foreign countries are subject to specific requirements. It must be explicitly pointed out that in each case the admission requirements of the universities precede the country assessments.
The country assessments provide information as to which upper secondary graduating certificates from which countries and under which conditions entitle the students to be admitted to the different Swiss universities. These assessments are for first-year students only. Further information is provided by the university concerned.
G. Conclusion
Thanks to the diverse opportunities within the Swiss education system, it can be distinguished by two characteristics:
its high degree of flexibility: there are several paths open to those who want to undertake training, change school or courses, or to complete another degree;
open access to the various educational opportunities: if they have the necessary qualifications, anyone can take the course of their choice and, in the case of higher education, also choose their field of study. The few limitations that exist are due, in the case of vocational training, to the supply of apprenticeship places and, in the case of certain branches of study, to the numerus clausus practised at some universities.
Although it may seem very complex, it is a well organised system that might require some reflexion over it. By choosing the Swiss Public Education, you will provide “open doors” to a wide range of opportunities for your children’s education.
If you have any questions, we have many Swiss experts that have first-hand experience with the Swiss education system that can provide you with all the answers to your questions. Thanks to our first hand experience, we will be able to guide your children on the best path for their studies and future career.
本文转载自雷梭勒家族办公室,如有侵权,敬请告知删除。
Sooswiss为您提供
瑞士方向私人管家式的定制服务:
1)家族传承 2)财富管理 3)瑞士投资
4)居留计划 5)税务优化 6)家族治理
更多资讯请登录网站 www.sooswiss.com
